(Editor Note: Insight Bytes focus on key economic issues and solutions for all of us. Please right click on images to see them larger in a separate tab. Click on the Index Topic Name at the beginning of each post to see more posts on that topic on PC or Laptop.)

Midwest farmers are declaring bankruptcy at a rate not seen since the Great Recession. As prices for corn, soybeans, milk and corn decline to decade lows, the Minneapolis Federal Reserve reports that Chapter 12 bankruptcy filings in 5 states of the Ninth District.
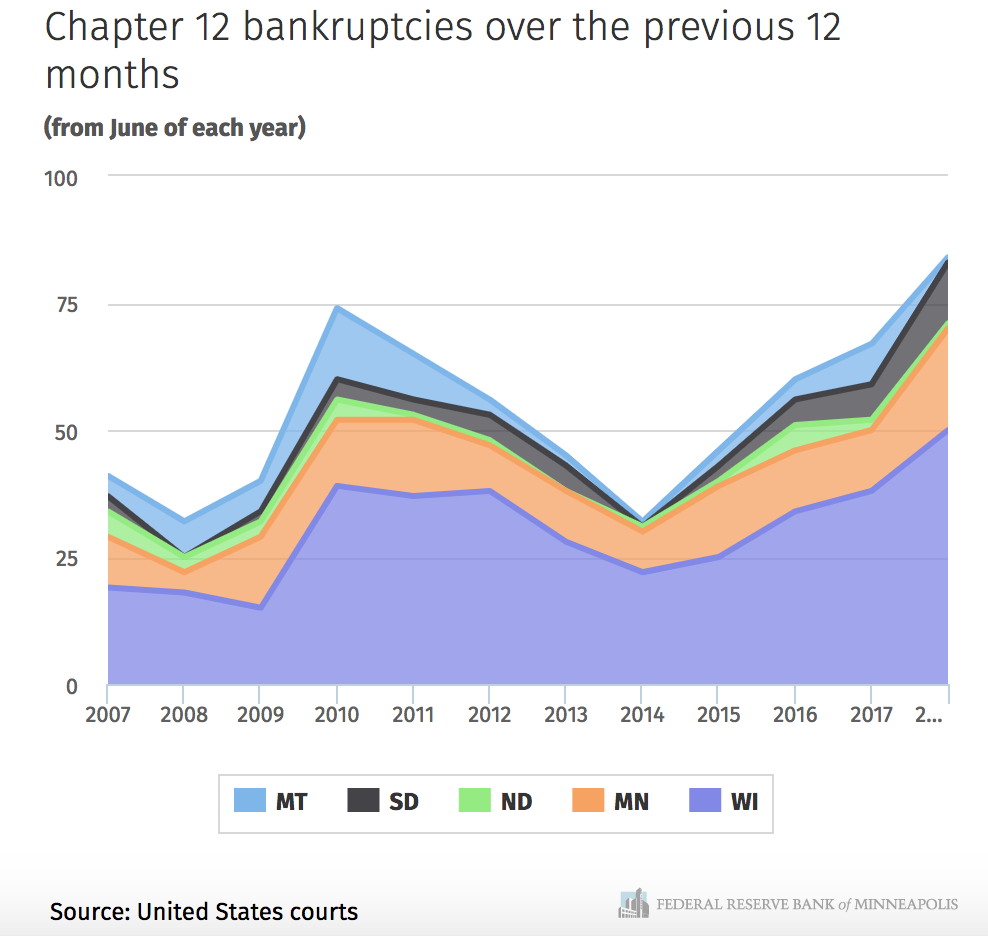
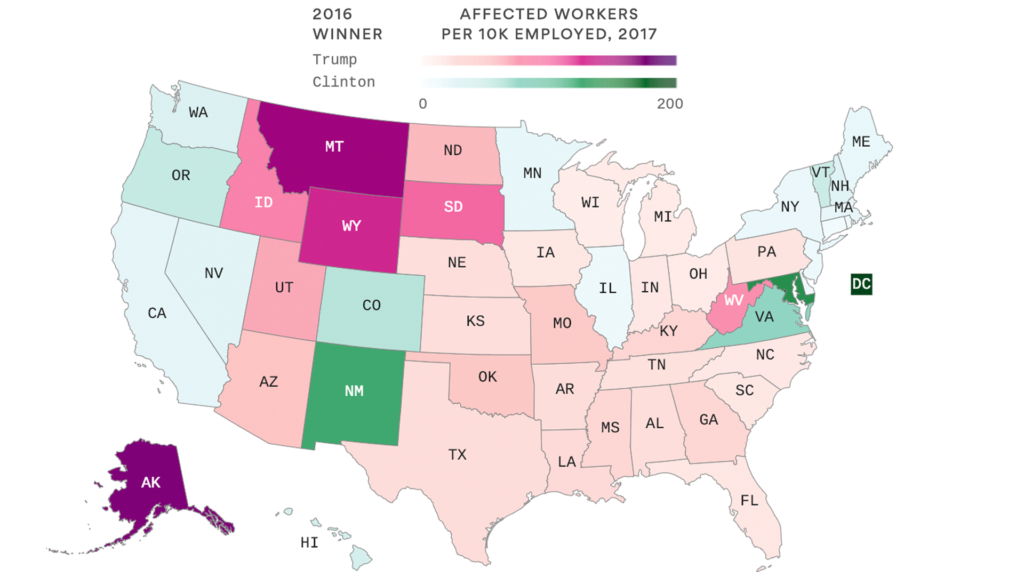
The Federal Reserve notes that based on the level of bankruptcies and the trajectory of the increase that bankruptcies will only increase. The government shutdown is exacerbating farmland pain. The Trump administration announced last summer $12 billion in farmer subsidies. But, because of the shutdown many farmers applying for subsidies and loans to plan for spring planting are not receiving the money they need. Many farmers and agriculture businesses are affected by the Department of Agriculture shutdown versus coastal states as shown below.
China turned to Russia and Brazil for soybeans in particular in the 4th Qtr of last year. US sales to China dropped to almost zero. As a negotiating tactic, China last week did pledge to buy more soybeans as traders in Chicago noted last week an increase in sales orders. However, when China switched purchases to major suppliers last year it will be difficult for US farmers to unhook those deals already in place. As one farm owner noted, “ it just seems like it’s one thing after another, over and over.”
Heartland challenges have actually been going on for years even before the Great Recession with the loss of millions of manufacturing jobs since China joined the WTO in 2000. The rural regions of the country have seen their wages grow at half the rate of metro areas. The opioid epidemic has cost thousands of young workers future careers, unemployment is twice what it is in the East and West. The digital internet infrastructure in rural areas is quite often at analog rates 4 times slower than broad band. Companies are at a disadvantage versus their metro competitors with slow bandwidth. Rural region hospitals are closing at an increasing rate leaving many rural people with hundred mile or more drives to the nearest emergency room. Life expectancy in Mississippi is the same as Libya. Heartland America has been left out the metro mainstream economy for the past 20 years. Our post – The Hallowing Out of Heartland America shows how rural regions have fallen behind in many infrastructure areas including: healthcare, Internet bandwidth, jobs, education with limited upward mobility for young people.
Next Steps:
The Heartland Venture Marshall Plan is similar in concept as the Marshall Plan deployed by the U.S. to rebuild the infrastructure of Europe after WWII, but instead of a government bureaucracy the Silicon Valley style innovation venture model is used. Venture development is designed to start small, build on successful prototypes and use multiple sources of funding to gain as much support as fast as possible to make the venture a success. Failure is part of the success fast, try several prototypes, do it, tweak it, try it again until it works or achieves the goals we set for the venture.
Here is a summary of the idea from our post of September 2017:
“We propose building a startup non-government organization. We are recommending a different approach by the Federal government to act as an investor in a non-government organization called a Heartland Development Center. An HDC acts as a central hub of critical services and infrastructure development while providing a continuous innovation system. The Heartland Development Center acts as a catalyst creating an innovation ecosystem to jumpstart local economics and social structures. HDCs would focus on all the key issues that a region needs to address to rebuild their economy and people’s lives: business formation, education and training, digital infrastructure, affordable housing, engaged local innovation media and health care.
The Federal government would seed the financing of these NGOs in key regions with additional funding from local and state governments, and major corporations who would benefit from the newly available job force tuned to their needs. HDCs would be ‘startup’ organizations installed at Land Grant universities bringing in leaders in their respective fields – ie. business formation – Y Incubator, preventive health – Cleveland Clinic, or training – Opportunity@Work as contractors to the HDC. These NGOs would establish continuously renewing innovation processes to stay in touch with their citizen – customers and businesses. Administration services would all be contracted using cloud software services for HR, Payroll, Training, Benefits and other internal systems to keep costs down. The HDC startups would be piloted in 3 non metro areas, where they would tune their business and socio economic models for maximum impact, then use those working models to implement HDCs in 25 or more other key regions for 5 – 10 years.”
Economists see the opportunity to invest in rural regions to jump start a part of the economy in innovative ways. Joseph Stiglitz, nobel prize winning economist for example advocates turning blue collar rural areas into ‘green collar’ hubs focused on developing innovative environmental technologies, systems and services.
Congress sees the need as well, as Congressman Ro Khanna – D-17 California is working on legislation patterned after the land grant college Morrell Act of 1862 to make an investment in technology job development in rural sections of the U.S. Khanna has supported computer programming training in West Virginia and toured the Midwest with Silicon Valley executives and venture capitalists to encourage investments in the Heartland. He points out that there is no need to send jobs to China, Brazil or India when there are people in our Heartland who can do those jobs well and at lower cost than expensive coastal regions.
There is one indicator of the desperation that many rural people feel is the fact that the opioid epidemic has a 50 % greater incidence in the Heartland than in our metro or coastal cities. We need to be building bridges through programs like the Heartland Venture Marshall Plan between our coasts and the inland empire to bring together our people developing consensus and shared experiences. Each HDC would be staffed by a equal mix of apprentice and college graduates from local rural education systems and metro university graduates. They would comprise a ‘Heartland Service Corp’ modeled on the AmeriCorp program with a benefit of complete forgiveness of student debt for two to four years of service depending on the debt balance. We would be building shared experiences of our young people to bridge the gap between inland and coastal cultures. These young people can innovate new opportunities to create an economic future that works for all.
